The elements that form the safety culture maturity model have been adapted from the safety culture components listed by the HSE in Reducing error and influencing behavior – HSG48. It is unlikely that these elements will map precisely onto the factors that companies have previously measured in safety culture or climate surveys because there is considerable variation in the proposed elements of an organization’s safety culture.
Some researchers argue that safety culture is composed of the safety attitudes of an organization’s employees. Others propose that it is much wider, incorporating systems, attitudes, values, beliefs, and organizational symbols. Safety climate tools tend to measure slightly different elements of safety culture. The elements used in the safety culture maturity model contain the most common components of both theoretical and measurement models.
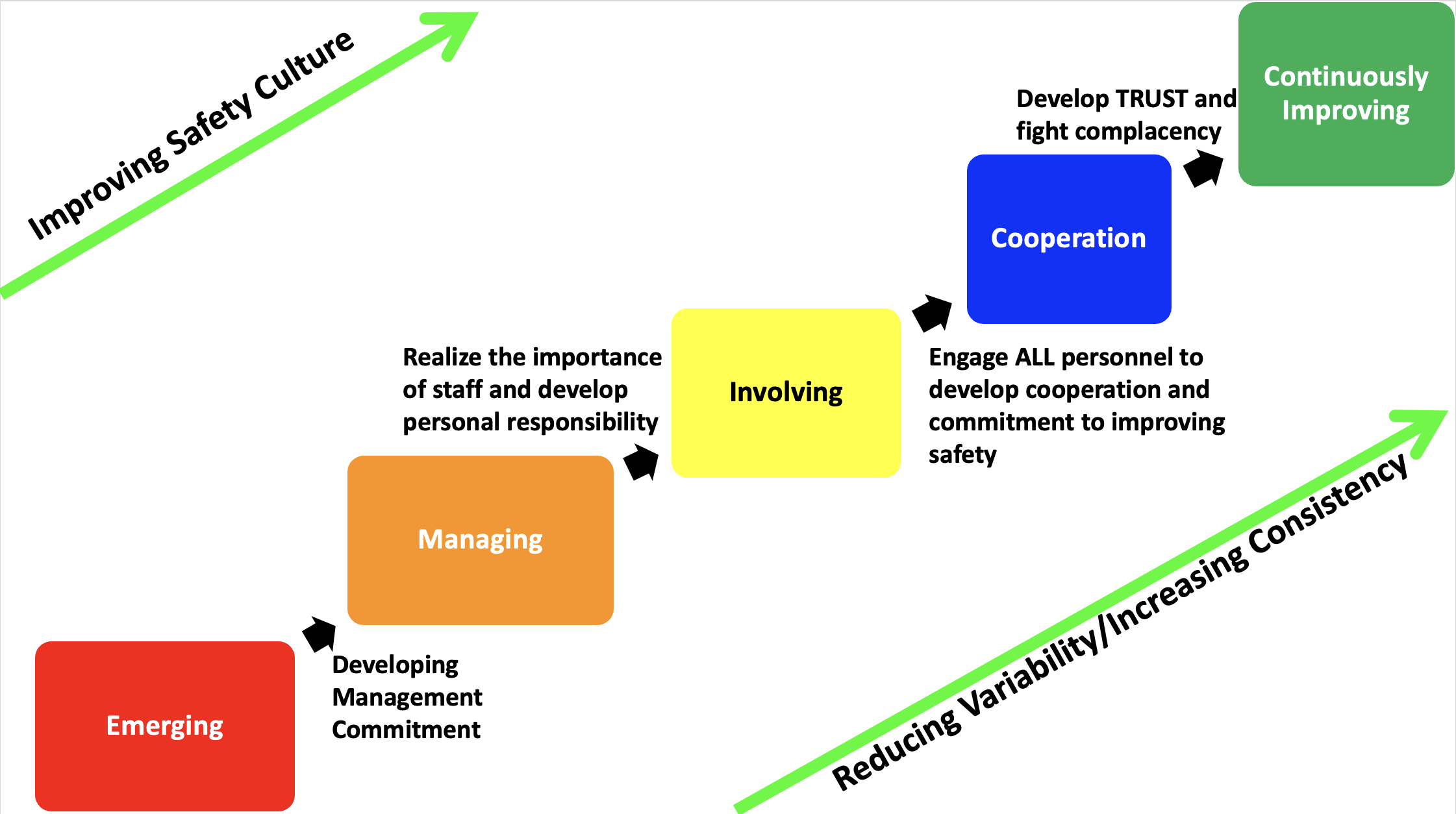
The safety culture maturity of an organization consists of the ten (10) elements described below. An organization’s LEVEL OF MATURITY is determined based on the maturity of these ten (10) elements. An organization will likely be at different levels on the ten components. Deciding which level is most appropriate will need to be based on the average level achieved by the organization.
CRITICAL NOTE: It is worth pointing out that Fleming (2001) warns that his model is ONLY APPLICABLE to organizations that meet the following criteria:
- having an adequate SMS
- most accidents not being caused by technical failures;
- complying to occupational safety laws and regulations; and
- using occupational safety as a way of preventing accidents