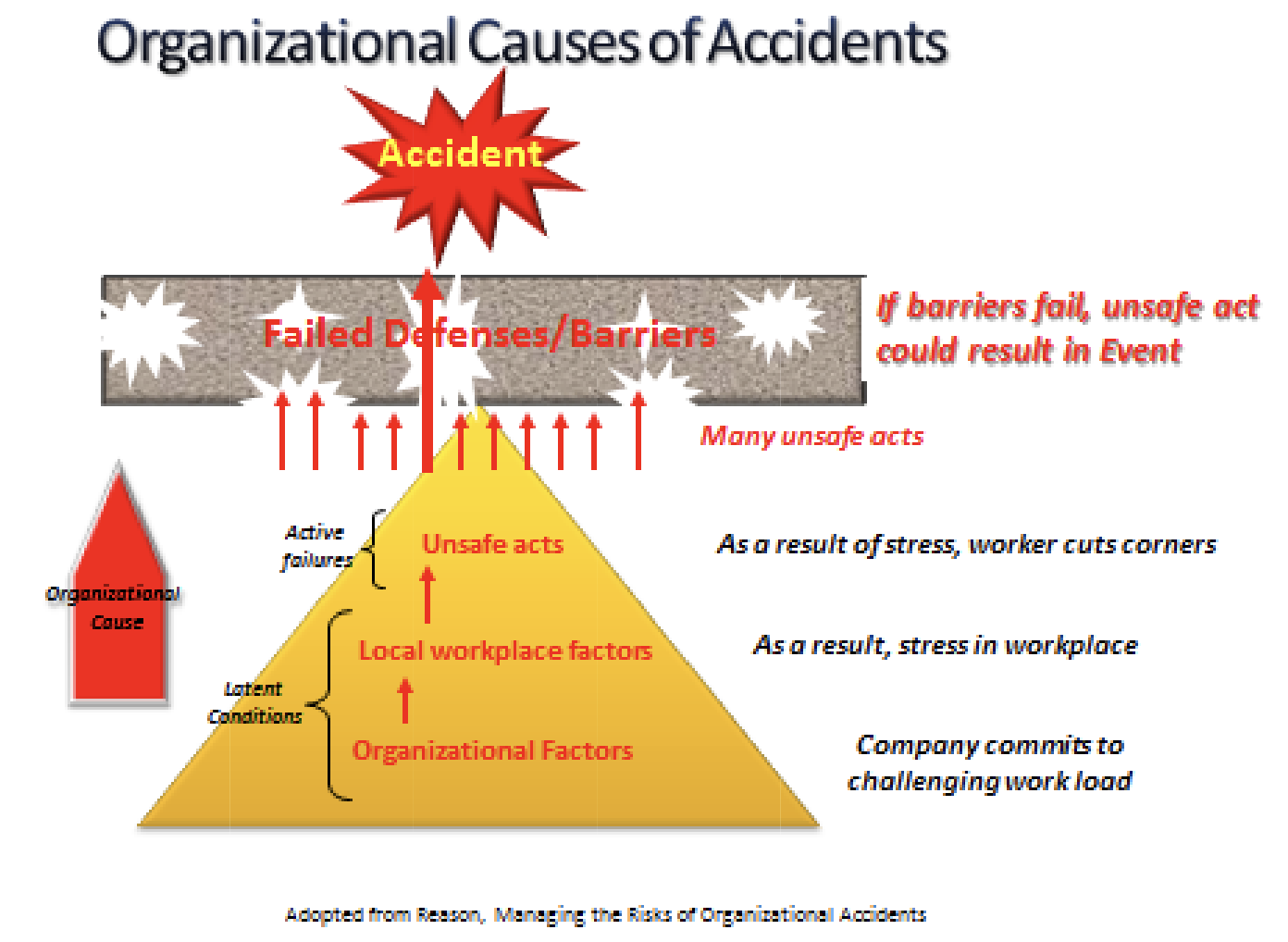
Building on my post from this weekend, discussing the three (3) pillars of Safety:
- Technical Safety
- SMS
- HOF/HOP
I wanted to share something I created for a client that needed to frame up the role of a safety professional within their organization. As in many immature safety cultures, safety people and even degreed, trained, and certified safety professionals can take on roles that DAMAGE the safety movement. For example, becoming a “safety cop”, which in some organizations is very easy to drift into for many in our profession. I know I did in my early days, but I was very fortunate to have worked for some great organizations and even better plant managers who corrected this flawed behavior immediately. I actually got “coached” and darn near disciplined for playing the “safety cop” role early in my career.
I have always thought that ANSI/ASSE Z590.2-2003 (R2012) Criteria for Establishing the Scope and Functions of the Professional Safety Position was an excellent starting point in defining our role within an organization. I even use this as the basis for “job descriptions” of existing safety roles and more importantly for new hires being considered for employment. It just seems that the safety professional’s role in an organization has become so diluted, that our primary skill set is not what it is being hired for – many want a “jack of all trades” rather than a safety professional. Here is my breakdown of how we should fit into the three (3) pillars of safety.
PLEASE NOTE: This is about the ROLE of the SAFETY pro(s) in the organization. If reading this, you realize your safety pros do not have the necessary skills to function within this capacity, you need to address this skill gap – not “dumb down” the role or job description!
This scope and functions are ESSENTIAL to Designing, Implementing, and Managing a world-class safety management system. Simply put, the scope and functions of the professional safety position should be to:
- Anticipate, Identify, and Evaluate hazardous conditions and practices
- Develop hazard control designs, methods, procedures, and programs
- Implement, Administer, and Advise others on hazard controls and hazard control programs
- Measure, Audit, and Evaluate the effectiveness of hazard controls and hazard control programs
Here are the details of each of these four (4) functions…