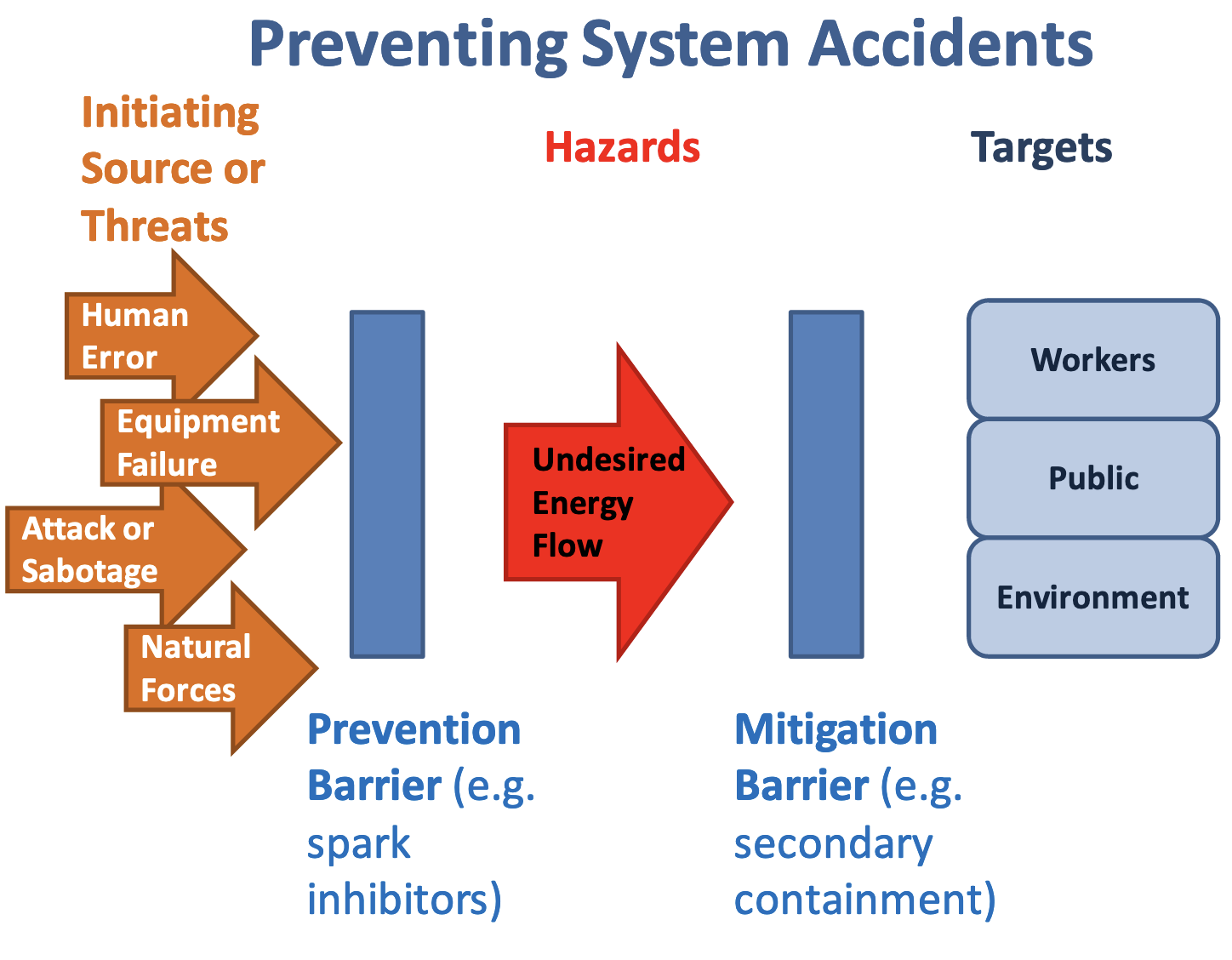
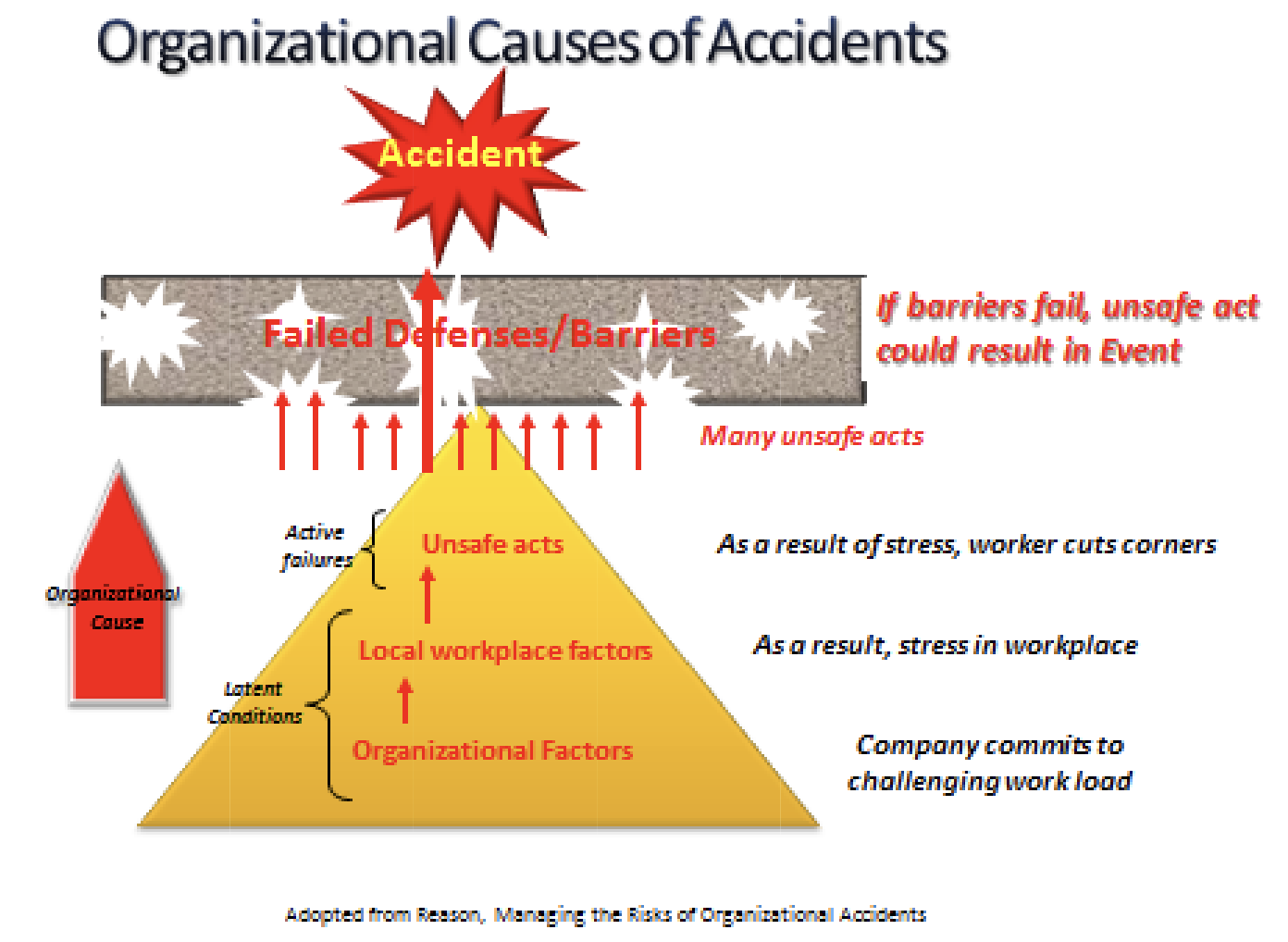
The use of risk controls or barriers to protect the people from hazards is a core principle of safety. Barriers are employed to serve two purposes:
- to prevent the release of hazardous energy and to
- mitigate harm in the event hazardous energy is released
Energy is defined broadly as used here and includes multiple forms, for example: Kinetic, biological, acoustical, chemical, electrical, mechanical, potential, electromagnetic, thermal, or radiation.
The dynamics of accidents may be categorized into five basic components, as illustrated below: